



EN 590 is a European standard that sets the specifications for diesel fuel quality. EN 590 diesel fuel is an ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) fuel, with a maximum sulfur content of 10 parts per million (ppm). This low sulfur content reduces emissions of sulfur oxides (SOx), which are harmful pollutants that contribute to acid rain and other environmental problems. EN 590 diesel fuel also has other specifications, such as density, flash point, cetane number, and distillation characteristics, to ensure efficient and safe combustion in diesel engines. The use of ULSD fuels like EN 590 diesel fuel with a maximum sulfur content of 10 ppm is an important step towards reducing the environmental impact of diesel engines and improving air quality.



Base oils like BS-150 Brightstock, SN-150, and SN-500 are often used as the primary component in lubricants, to which various additives are added to improve their performance properties. The choice of base oil depends on the specific requirements of the lubricant application, such as the operating conditions and the type of equipment being used.
Overall, base oils are a critical component of lubricants and play a key role in protecting machinery and reducing friction and wear. The use of high-quality base oils, along with effective additive packages, can help to extend the life of machinery and improve overall efficiency.
Lubricants are substances that are used to reduce friction and wear in machinery and engines by providing a protective film between moving parts. They are categorized into three main categories: automotive, marine, and industrial lubricants. Automotive lubricants include engine oils, transmission fluids, gear oils, and brake fluids, and are formulated to meet the specific requirements of different types of engines and operating conditions. Marine lubricants are designed to withstand harsh marine environments, while industrial lubricants are used in a wide range of equipment and are formulated to meet specific requirements. The use of high-quality lubricants can extend the life of machinery, improve efficiency, and reduce maintenance costs.
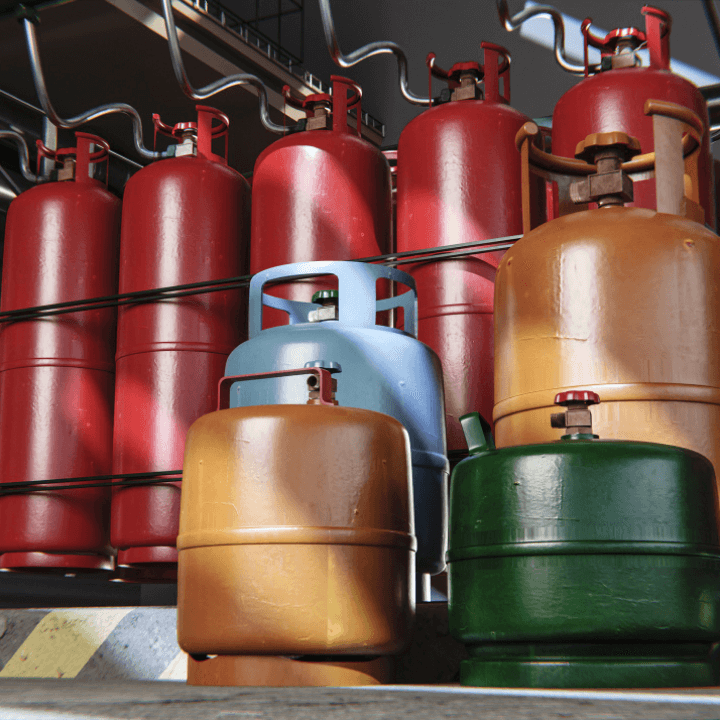



LPG (Liquified Petroleum Gas) is a mixture of propane and butane gases that are compressed into a liquid form for easier storage and transportation. It is a cleaner-burning fuel than coal or oil and is used extensively in residential, commercial, and industrial applications, such as heating, cooking, and manufacturing processes. LPG is also used as a fuel for vehicles in countries where natural gas infrastructure is limited. While LPG has many advantages, it is not a renewable resource and its use contributes to climate change. Therefore, efforts to transition to cleaner, renewable energy sources should be prioritized to mitigate environmental concerns.